Therapeutic exercise: its role in restoring and maintaining physical well-being
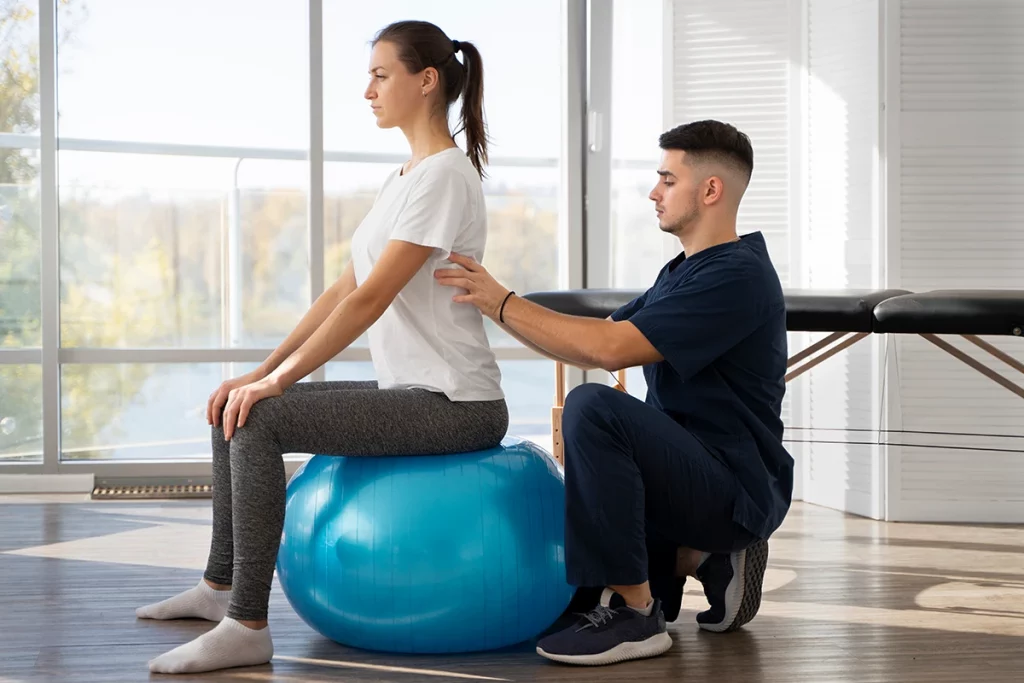

Therapeutic exercise is a key pillar in the management and recovery of a wide range of medical conditions. It is a multidimensional approach, usually administered by a physiotherapist, which aims to improve the function, mobility and quality of life of patients through targeted and supervised physical activity. It is important to understand the crucial role it plays in addressing health and wellness challenges.
What is therapeutic exercise and why is it important?
Therapeutic exercise, also known as exercise therapy, is a form of non-drug treatment that focuses on performing controlled physical movements to improve body functions. This approach is widely used in a broad range of medical conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders, cardiovascular, neurological and respiratory diseases. The main objective of therapeutic exercise is to improve the patient’s function and independence, reducing pain, increasing mobility and preventing long-term complications.
What is Medical Exercise Therapy?
Medical Exercise Therapy (MET) is a specialised branch of exercise therapy that focuses on devising and implementing bespoke exercise programmes to treat specific medical conditions. This approach is based on scientific principles and clinical evidence to optimise therapeutic outcomes. Using advanced assessment techniques and specific exercise protocols, experienced MET physiotherapists are able to provide highly targeted and effective treatments for a wide range of conditions.
What are the core components of therapeutic exercise?
The core components of therapeutic exercise include:
- Initial assessment
- Treatment planning
- Performance of exercises
- Assessment of results
The initial assessment is essential to understand the patient’s needs and abilities, as well as to identify areas of weakness and functional limitations. Based on this information, the physiotherapist can develop a bespoke exercise programme that aims to improve the patient’s strength, flexibility, balance and coordination.
How to structure a therapeutic exercise
Structuring a therapeutic exercise requires a combination of resistance exercises, stretching, joint mobilisation and functional activities. It is important to adapt the programme to the specific needs of the patient, taking into account their age, physical condition, underlying pathology and therapeutic goals. Exercise programmes can be gradually adapted and modified according to the patient’s response and progress over time.
What is the objective of therapeutic exercise?
The main objective of therapeutic exercise is to improve the patient’s function and independence, reducing pain, increasing mobility and preventing long-term complications. Moreover, therapeutic exercise can help reduce the risk of relapse and improve the patient’s overall quality of life. Through a gradual and targeted approach, therapeutic exercise can help patients achieve and maintain their long-term health goals.
Conclusions and role of the physiotherapist in therapeutic exercise
To conclude, the role of the physiotherapist in therapeutic exercise is vital. The physiotherapist not only devises and supervises the exercise programme, but also plays an educational role in giving the patient the knowledge and skills needed to continue to manage their long-term condition. With the expert guidance of the physiotherapist, therapeutic exercise can become a powerful tool for recovering and maintaining health and well-being. It is crucial that patients carefully follow the physiotherapist’s instructions and actively engage in their exercise programme in order to maximise therapeutic benefits.